What Is the Word That Describes an Enzyme Being Altered
The word allosteric when used to describe enzymes such as allosteric enzymes implies _____. Read more about allosteric control.
Enzymes Review Article Khan Academy
The study of enzymes is called enzymology and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual pseudocatalytic properties.

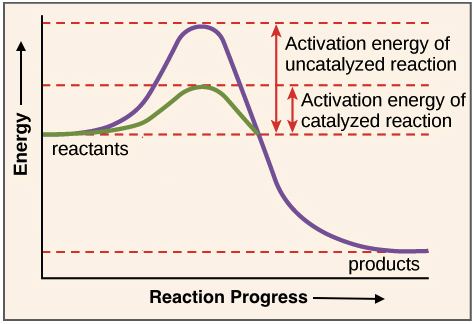
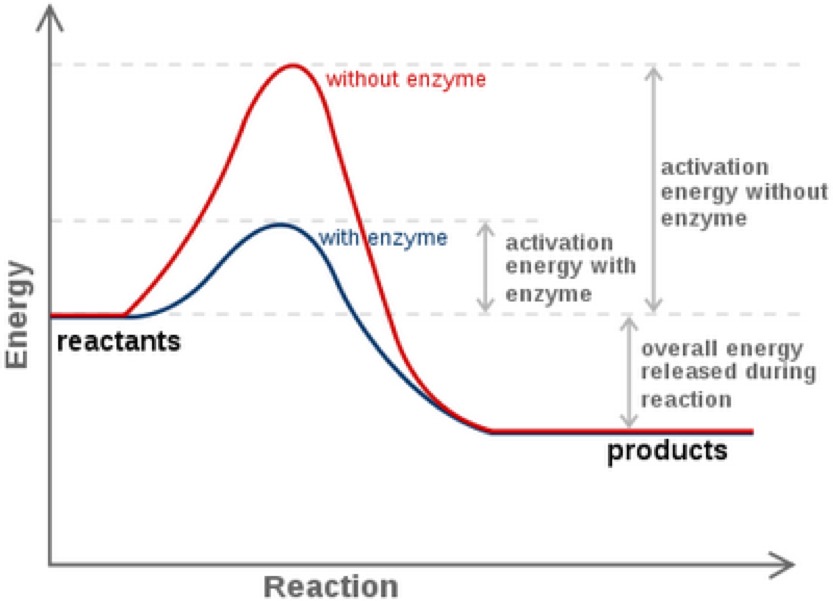
. The word induction when used to describe enzyme induction is in reference to amphilbolism What term is used to describe the link between anabolic and catabolic reactions where immediate metabolites can move between the reactions. Enzymes are catalysts in biological systems that lower the activation energy so that molecules can begin reacting with each other. Enzymes speed up reactions they act as catalysts.
In the body oxygen. An enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process. Most enzymes are proteins and most such processes are chemical reactions.
The biological processes that occur within all living organisms are chemical reactions and most are regulated by enzymes. Catalytic enzymes break down the toxic hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. Enzymes are made from amino acids.
The binding together of an enzyme and a substrate forms what. Denaturing an enzyme results in a permanent change to that enzyme. Enzymes are catalysts that increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed themselves in the process.
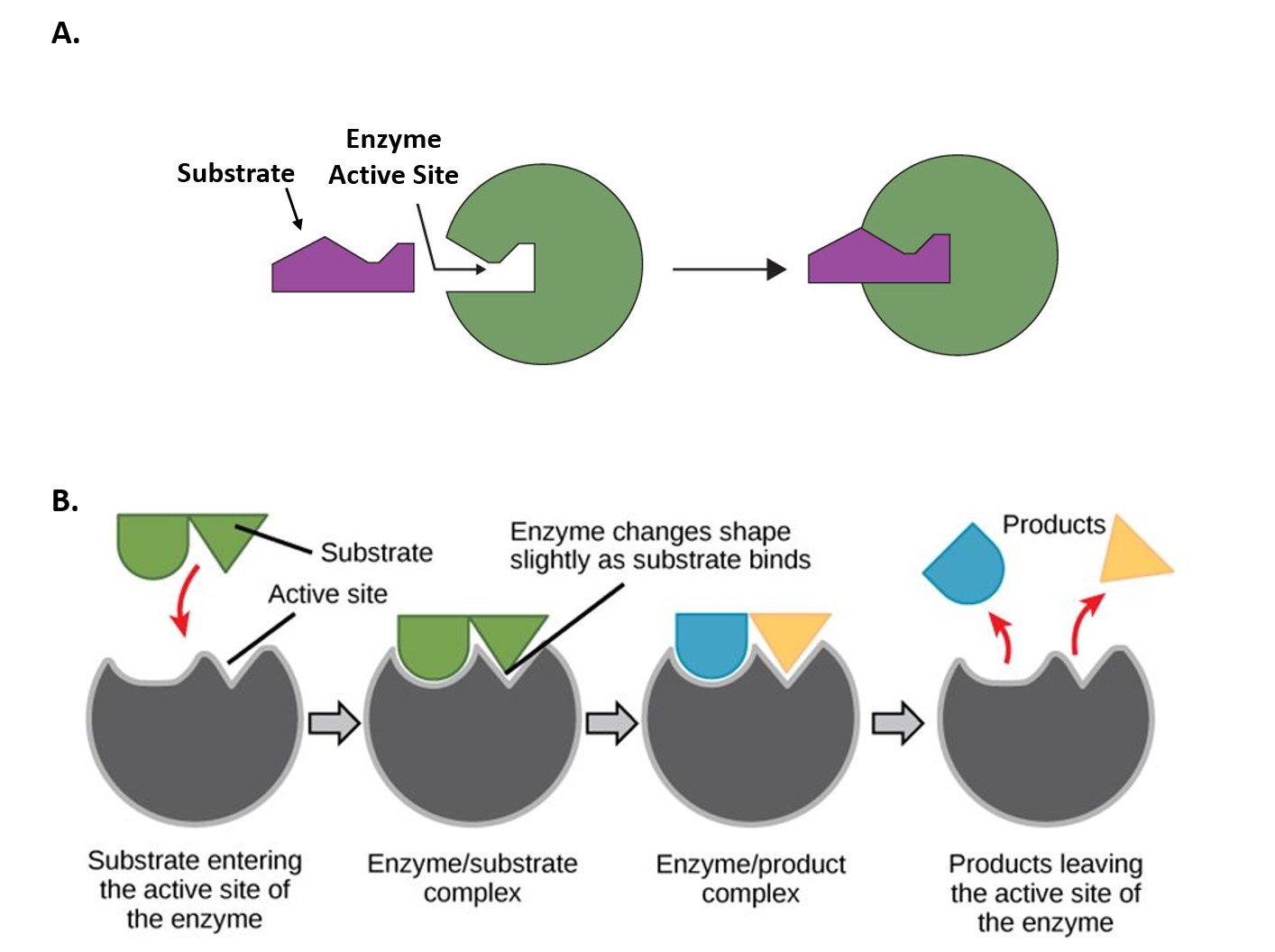
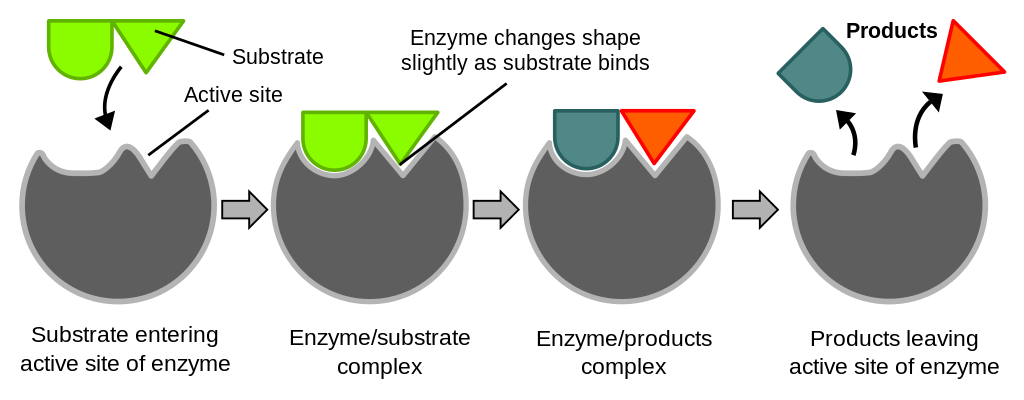
The substrate and enzyme form an enzyme substrate complex The bonds in the substrate are altered so that the substrate changes into the products 5The products leave the active site. When an enzyme is denatured it can lose some of its original properties and may not be able to perform its natural functions. An enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process.
Most enzymes will become denatured at. The permanent change comes from heat changing the shape of the enzyme which stops it from. Salts and acids are examples of inorganic compounds called __________ which dissociate in.
Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by a biological molecule an enzyme. It is ready for a new substrate molecule. Enzyme a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process.
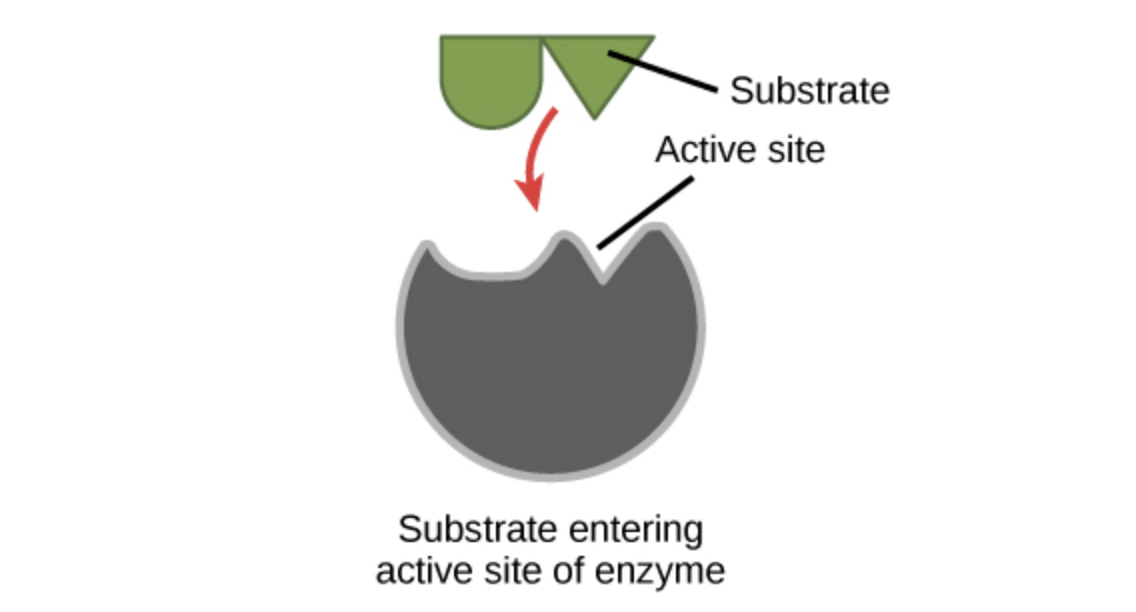
The fact that they arent changed by participating in a reaction distinguishes catalysts from substrates which are the reactants on which catalysts work. Site on the enzyme where the chemical reaction takes place. For full treatment see protein.
An enzyme may be denatured by high temperatures. Is produced by cells. A adding amino acids from the carboxylterminal end of the polypeptide in digestion.
An enzyme is one such catalyst which is commonly known as the biological catalyst. A denatured protein cannot do its job. When enzymes denature they are no longer active and cannot function.
Reacts with water to form carbonic acid. Enzyme a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process. A question on what they are made up of the simple answer of protein will be.
Within the enzyme generally catalysis occurs at a localized site called the active site. Enzymes are made up of protein. The enzyme including its active site will change shape and the substrate no longer fit.
A brief treatment of enzymes follows. Is used during cellular respiration. An example of an enzyme being named by ase being added to a word the describes the reaction is carboxypeptidase and it means.
Denaturation is the term used for any change in the three-dimensional structure of a protein that renders it incapable of performing its assigned function. Enzymes rely on having a very specific three-dimensional structure to work right. This is called the induced fit model 3.
Extreme temperature and the wrong levels of pH -- a measure of a substances acidity or alkalinity -- can cause enzymes to become denatured. Literally an enzyme is a protein substance produced in living cells that influences a chemical reaction within a plant or animal without being changed itself World Book Dictionary. During a chemical reaction a catalyst remains unchanged both in terms of quantity and chemical properties.
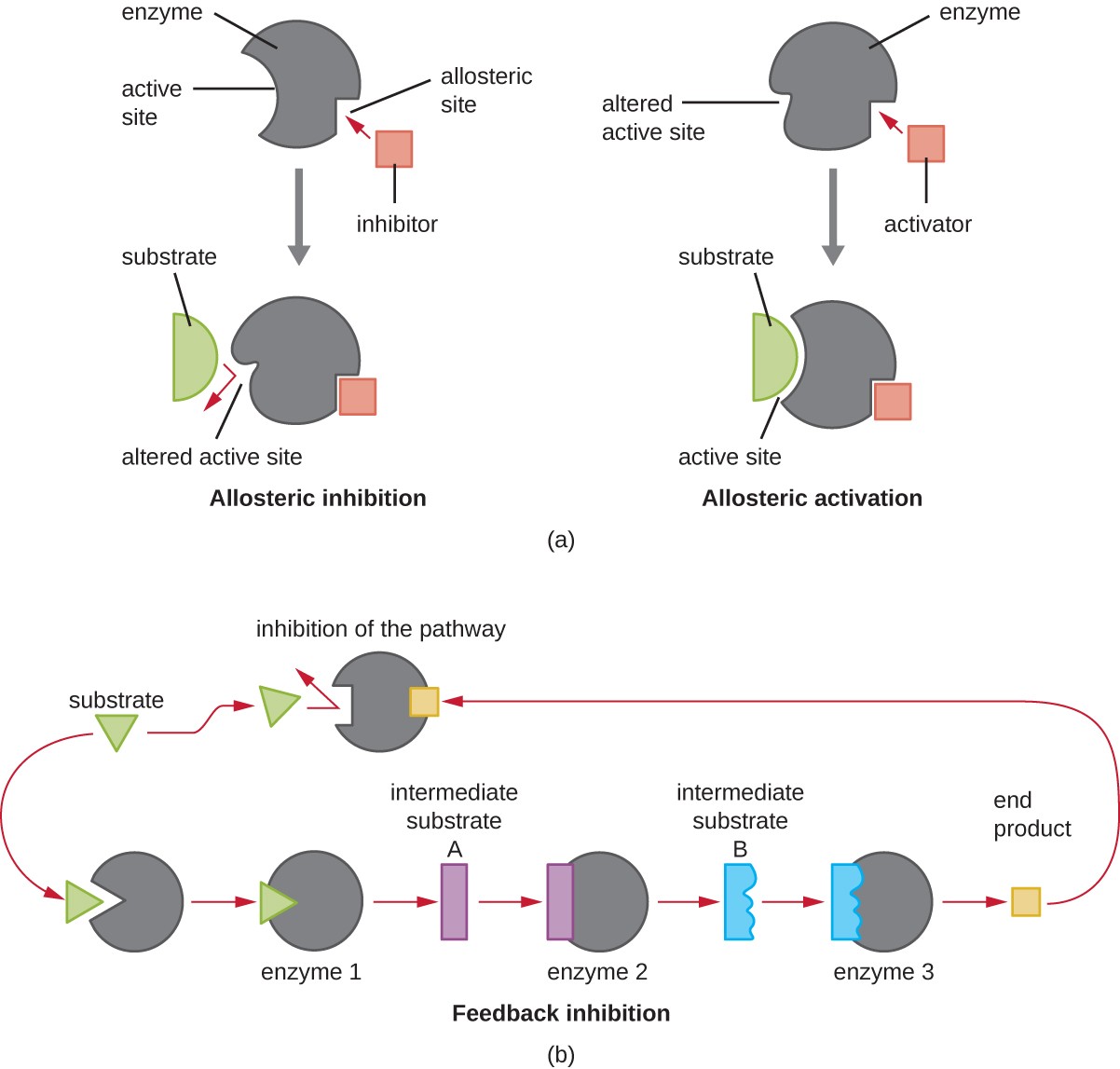
The enzymes shape can be controlled The activity of an allosteric enzyme is altered by a small molecule known as an _ effector. The rate of reaction will be affected or the reaction will stop. Enzymes are catalysts that increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed themselves in the process.
As with many scientific words the word enzyme hails from the Greek. Badding amino acids from the carboxylterminal end of the polypeptide in respiration. Is used during cellular respiration.
Since enzymes have a very selective active site if the enzyme shape is changed or denatured it wont allow the enzyme to bind. Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions. This enzyme model describes how one enzyme fits one substrate the same.
Amino acids are a type of protein but if ever asked. Our definition is a bit broader. Similarly you may ask what are used to make enzymes.
Sometimes denaturation is equated with the precipitation or coagulation of a protein. If the temperature around an enzyme gets too high the enzyme loses its shape which is known as denaturation and ceases to work. A catalyst is a chemical that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being changed by the reaction.
Enzymes work consistently until they are dissolved or become denatured. A graph to show the effect of. Catalysis is the phenomenon by which the rate of a chemical reaction is altered enhanced without changing themselves.
This describes any substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed itself. They are NOT the same. Many enzymes require the presence of small non-protein units or cofactors to carry out their particular reaction.
The enzyme remains unchanged and the active site returns to its original shape. The biological processes that occur within all living organisms are chemical reactions and most are regulated by enzymes. Is a major electrolyte.
The substrate is the chemicalcompound being altered by the action of the enzyme. These three letters at the end of the word indicate the substance is an enzyme.

Enzyme Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Metabolism End Product Inhibition Britannica

Enzyme Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Protein The Mechanism Of Enzymatic Action Britannica

Managing Enzymes In Food Basics Of Enzyme Science Foodcrumbles
Energy Matter And Enzymes Microbiology
Enzymes Review Article Khan Academy

Enzymes Biology For Non Majors I
Chem4kids Com Biochemistry Enzyme Regulation

Enzyme Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Enzyme Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

The Crispr Revolution Hopes Huntington S Disease Information Medical Laboratory Science Teaching Biology Laboratory Science
Ch103 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions In Biological Systems Chemistry


Comments
Post a Comment